Muscle building after intervertebral disc surgery: It is estimated that every second visit to the family doctor in Germany is due to spinal problems. Around 180,000 people suffer a herniated disc every year, of which around 80,000 sufferers undergo spinal surgery.
Other, often associated clinical pictures such as narrowing of the spinal canal also often lead to surgery.
Due to the immense importance of the spine for the individual's ability to move and be active, follow-up treatment and aftercare following a surgical procedure are aimed at completely restoring all functions in the spinal area.
The surrounding muscles in the entire back area play a key role. This article addresses, among other things, the question of how to build muscle as quickly as possible after disc surgery and how you can build up enough mass .
The main focus is on the importance of nutrition, lifestyle and training.
For more great tips on the subject of a fit and strong back , please take a look at Backfit !

The intervertebral discs: Intervertebral discs - anatomy, function and disorders
The spine forms the central axis of our body. The healthy spine in the shape of an S-curve allows movements and activities in a wide variety of directions with stable alignment.
However, the spine does not stand alone as a homogeneous anatomical structure. It fulfills its function in a complex interaction of bones, ligaments, tendons, intervertebral discs, nerves and muscles .
24 vertebrae form the basis of the spine . 7 are located in the neck area, 12 in the chest area and 5 in the loin area. There are another 10 vertebrae in the sacrum and coccyx area .
However, the lumbar area grows into an entire, strong bone block up to the age of 25. The intervertebral discs are special anatomical elements that lie between the vertebral bodies and connect them into a double S shape .
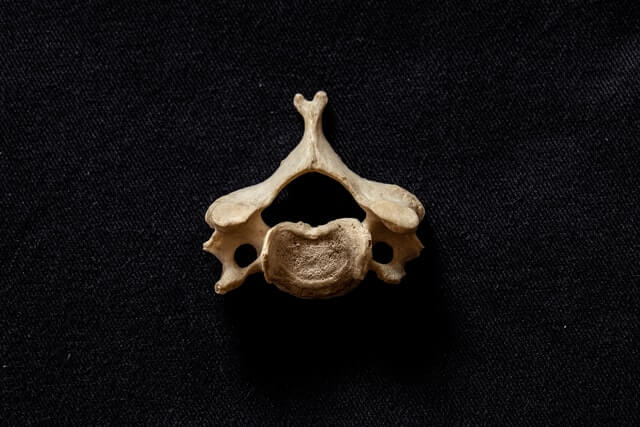
Anatomical basics and impairments
Intervertebral discs are flexible structures made up of cartilaginous fibers. The spine has 23 of them. Each intervertebral disc consists of two parts . An outer fibrous ring encloses an inner bile core.
The gelatinous tissue of the inner core consists of 80-85% water. This water is bound by certain protein structures . A kind of water cushion is created.
This indicates the function of each disc: The cushions form an elastic pressure cushion and enable the mobility of the spine .
It is important that at the end of the 20th year of life - the person is now fully grown - the discs no longer have any blood vessels . Only when there is an alternation of stress and relief do the cores absorb liquid again and supply themselves with nutrients.
With every load, the cores lose fluid. When a disc herniates, part of the gelatinous mass breaks out of the core through the outer fibrous ring. This can lead to pain if, for example, nerves are pinched.
How do herniated discs occur and how serious are they?
The suppleness of the outer fiber rings decreases with age. This process begins at the age of 40. Overloading, poor posture and predominantly sedentary work also promote herniated discs .
In some cases, hereditary factors also play a role. Those affected then have a certain predisposition to protruding intervertebral disc mass .
Many of those affected are not aware that they have breakthroughs in the outer fiber rings. If the material coming out does not press on nerves or other important elements, pain will not necessarily occur.
How serious the incident is in individual cases cannot therefore be assessed in a standard manner. The different impairments after incidents also mean that surgical intervention is not necessary in every case.
However, it is important that there is some relief for the affected sections of the spine. This is where well-developed and strong muscles in the entire back area come into play.

The importance of muscles and actively preventing damage
The muscles protect the entire spine to a certain extent and relieve it. It also helps ensure that the movements are carried out in accordance with the anatomy and not with poor posture.
Their supportive nature should not be underestimated either. For example, in the event of vertebral fractures and incidents, they can ensure that nerve cords are not pinched .
The dreaded spinal duct stenosis described above is usually also associated with a lack of muscles in the spinal area , as supporting elements are then missing.
After a herniated disc, muscle building training is always the method of choice for conservative therapy. Conservative therapy means that no surgical intervention is carried out.
Rather, the consequences of a herniated disc are counteracted through physiotherapeutic measures and strengthening the muscles.
It should be emphasized once again that muscles do not only play a role when the damage in the form of a herniated disc has already occurred.
In principle , strong muscles in the entire spinal area can help to actively prevent complaints and damage. The older we get, the more we lose muscle.
To maintain health in the spine area, it can be interesting to work specifically and permanently on building muscles . This saves many people serious problems in the spine area. The muscles also help to maintain mobility in the back at a more youthful level.

Building muscle after intervertebral disc surgery
In the case of severe herniated discs , in which structures such as nerves have been affected, those affected cannot avoid surgical intervention.
This is often a form of relief surgery in which certain overstressed areas or pinched nerves have to be relieved of their stress.
The need for spinal surgery may also arise if the spinal injury is the result of an accident or a sports injury, for example.
In these cases it is often not possible to restore mobility and freedom from pain without surgical intervention. An essential part of rehabilitation measures after the procedure is building muscle .

Training and therapy methods in different time periods
As a rule, the rehabilitation measures after the procedure include very different measures. Some things begin when the patient is still bedridden. The aim here is to mobilize him in general and perhaps also to stabilize his breathing.
The next step is usually to restore everyday mobility. Only then can targeted training measures that include muscle building measures be followed.
There are no standard recommendations for muscle training after spine surgery. This has, among other things, to do with the fact that those affected enter the training with very different requirements in terms of fitness and body structure.
A trained athlete has a different performance level than an untrained or older person. Building muscle in old age after spinal surgery must therefore be precisely tailored to the performance, level of training, physical requirements and motivation of those affected.
It should also be taken into account that untrained people can initially build muscle mass faster, even with little training, than people who have already trained intensively. Here the training stimuli often have to be less intense.
Diet and lifestyle
If you want to build muscle as quickly as possible after an operation in the spine area , other factors in addition to training activities cannot be neglected. On the one hand, nutrition also plays a role in building muscles.
On the other hand, a specific lifestyle has often led to complaints and damage to the spine area . This lifestyle often resulted in there not being enough muscles available to protect spinal elements.
If such a passive lifestyle is maintained after the operation , even short-term measures to build muscle will be of little use. The next disc operation may then already be foreseeable.

Protein supply and muscle growth
Proteins and therefore their smallest building blocks, the amino acids , are indispensable for muscle growth . Proteins form the building material for all body tissues and therefore also for the muscles.
Proteins are substances that are subject to constant transformation processes in the human body. We distinguish between essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids .
The former must be supplied to the body again and again with food, because our organism cannot produce them itself.
Other building blocks are put together by the body itself, but many other substances such as certain enzymes and other protein building blocks must also be present in sufficient quantities for their formation.
Protein requirements can vary greatly from person to person. Recommendations range from 0.8 g kilogram body weight to 1.6 g/kg body weight in special life situations. In addition, not all protein is the same. Some proteins are easier for the human body to utilize than others.
The building and remodeling processes in the body can be slower in older people and use up more resources. That's why health experts recommend that older people pay attention to their protein intake .
This is particularly true in the follow-up treatment after operations and therefore also after spinal operations. If you don't pay attention to your protein supply after spinal surgery, you won't be able to lose weight or build muscle even with intensive training.

Muscles may even be more likely to break down because the organism relies on the protein in the muscles if there is insufficient protein intake. For this reason, a low-calorie diet is a bad idea when it comes to building muscle .
This is at least the case if this diet is not associated with sufficient protein intake and muscle building . For some people, diets are part of their lifestyle.
Without realizing it, this lifestyle can be detrimental to spinal health . Not only too little exercise, but also too little protein can promote degenerative changes in the spine.
Building muscle after intervertebral disc surgery: provide training stimuli
Muscles - for example after a relief operation - can be built up in various ways through training. In general, muscles build up when stress stimuli and recovery phases alternate.
When we talk about muscle growth , we are talking about a thickening of the existing muscle fibers. All muscle growth is, in a way, an adaptive response. The muscle reacts to stimuli and prepares itself to withstand stronger stimuli in the future.
During aftercare after a surgical procedure on the spine , muscle stimuli can be applied in different ways .
Something to think about here is:
- Swimming and other training in water such as aqua fitness
- isometric exercises (exercises that use your own body weight)
- Strength training
- rowing
- Back exercises
- more exercise in everyday life
- certain forms of yoga
- Pilates
For some groups of people, training measures and exercises do not only involve direct stimuli to the muscles in the back area. This can also involve coordination and balance exercises that help stabilize the entire spinal area .
In order to avoid poor posture in the future, it is also important to train how some movements are carried out. It is possible that the wrong muscles are often used for certain movements and that this causes them to be overwhelmed.
Certain movement concepts such as Feldenkrais start at exactly this point.

Special training concepts can, but do not have to be, necessary
As already described, there is no such thing as training after spinal surgery. The rehabilitation measures must be tailored to the individual requirements of the individual affected.
There are special training concepts such as Kieser training that focus on the spine area and the development of muscles in this physical area. Kieser training is strength training that particularly focuses on back health .
For some people, a special training concept may be right, for example to build and maintain back muscles after a herniated disc .
You don't necessarily have to complete these programs, which are usually expensive and come with a membership in a specific training facility, in order to get fit and strengthen your back muscles after spinal surgery .
During rehabilitation measures after the procedure, physiotherapists usually show those affected a series of exercises and measures that can be easily integrated into everyday life.
In the end, the only important thing is that the combination of training, lifestyle and nutrition does more for the neglected back muscles than was usually the case before the operation.
Ideally, you will now remain active throughout your life in order to prevent further herniated discs and similar events. Strengthen your back and regularly build muscle after intervertebral disc surgery .
